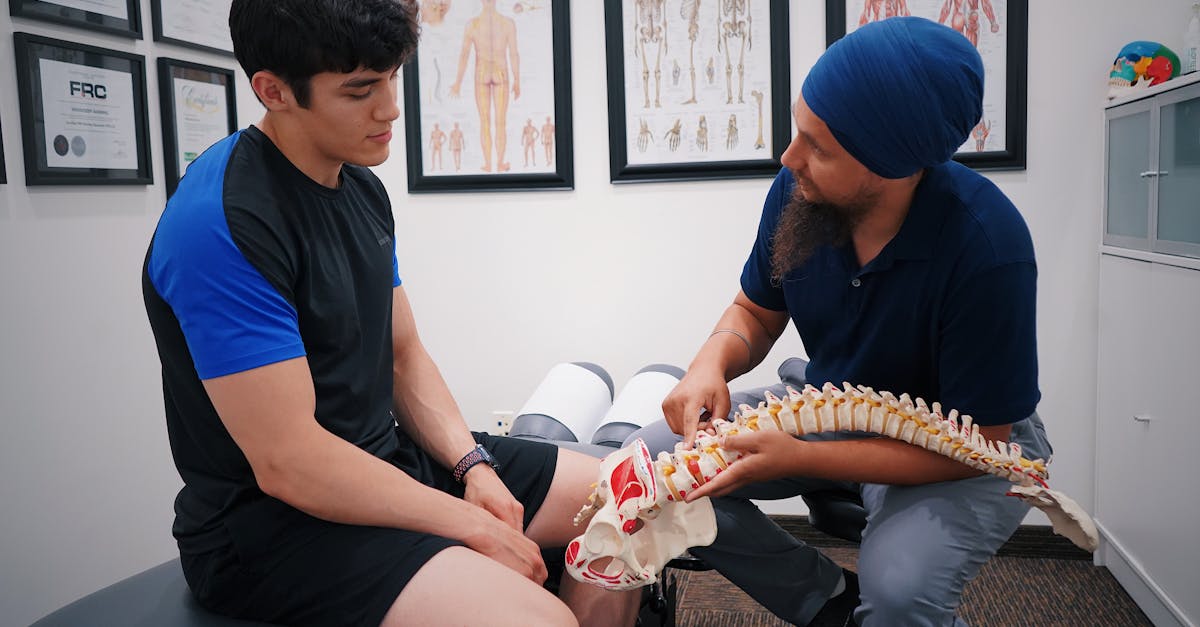
Can you increase bone density?
Medical Treatments for Low Bone Density
When it comes to treating low bone density, medical interventions can play a crucial role in helping to improve bone health. Healthcare professionals often prescribe medications such as bisphosphonates, denosumab, or teriparatide to help increase bone density and reduce the risk of fractures in individuals with osteoporosis or osteopenia. These medications work by either slowing down bone breakdown or stimulating new bone formation, ultimately leading to stronger bones.
In some cases, hormone therapy may also be recommended to help improve bone density in individuals, especially postmenopausal women. Hormone therapy can help to balance estrogen levels, which are important for maintaining bone health. However, it's essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits of hormone therapy with a healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Options like medication and hormone therapy
Medication and hormone therapy are common options for individuals looking to increase their bone density. Medications such as bisphosphonates, denosumab, and teriparatide are often prescribed to help strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures. These medications work by either slowing down bone breakdown or stimulating new bone formation, ultimately improving bone density.
Hormone therapy, particularly for postmenopausal women, can also be beneficial in increasing bone density. Estrogen therapy, for example, can help maintain bone strength by slowing down bone loss. However, hormone therapy may not be suitable for everyone and should be discussed with a healthcare provider to assess the risks and benefits. It is important to note that these treatments are typically used in conjunction with lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet and regular exercise to maximize their effectiveness in improving bone density.
Preventing Bone Density Loss
To maintain optimum bone density and prevent loss as you age, it is essential to engage in regular weight-bearing exercises. Activities such as walking, dancing, hiking, and weightlifting help stimulate bone growth and strengthen bones. Incorporating these exercises into your routine can significantly reduce the risk of developing osteoporosis and fractures related to low bone density.
Another crucial factor in preventing bone density loss is ensuring an adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D through a balanced diet or supplementation. Calcium is vital for bone strength, while vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium efficiently. Foods rich in calcium include dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods, while vitamin D sources include fatty fish, egg yolks, and sunlight exposure. By maintaining a healthy diet rich in these nutrients, you can support bone health and reduce the likelihood of bone density decline.
Strategies for maintaining bone health as you age
As you age, it becomes increasingly important to focus on maintaining your bone health to prevent issues related to low bone density. One effective strategy is to engage in weight-bearing exercises regularly. Activities such as walking, jogging, dancing, and strength training help to strengthen bones and improve overall bone density. Aim for at least 30 minutes of weight-bearing exercises most days of the week to promote bone health.
In addition to exercise, ensuring an adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is essential for maintaining strong bones. Calcium is necessary for bone mineralization, while vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium efficiently. Include dairy products, leafy greens, nuts, and fortified foods in your diet to meet your calcium needs. Exposure to sunlight is also a natural way to boost your vitamin D levels. By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can proactively support your bone health as you age.
Monitoring Bone Density Progress
Regular monitoring of bone density is crucial for individuals at risk of low bone density or osteoporosis. Bone density scans, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans, are commonly used to assess bone health. These scans provide detailed information about the mineral content in the bones, allowing healthcare providers to evaluate the risk of fractures and determine the effectiveness of treatment plans.
Most healthcare professionals recommend bone density scans every 1-2 years for individuals at risk. This frequency can help track changes in bone density over time and detect any significant decreases that may require intervention. By staying proactive with bone density monitoring, individuals can work with their healthcare team to establish appropriate preventive strategies and treatments to maintain or improve bone health.
Importance of regular bone density scans
Regular bone density scans play a crucial role in monitoring the health of your bones. These scans provide valuable information about the density and strength of your bones, helping to identify any potential issues or abnormalities early on. By regularly monitoring your bone density through scans, healthcare providers can track changes over time and make informed decisions about treatment or preventive measures.
Early detection of low bone density can help prevent serious complications such as fractures or osteoporosis. Regular bone density scans allow for timely intervention and management of bone health issues before they progress to more severe conditions. It is essential to follow healthcare recommendations regarding the frequency of bone density scans based on individual risk factors and medical history to maintain optimal bone health and overall well-being.
FAQS
Can bone density be increased?
Yes, it is possible to increase bone density through various lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and medical treatments.
What are some medical treatments available for low bone density?
Medical treatments for low bone density may include prescription medications, hormone therapy, and other interventions recommended by healthcare providers.
How can one prevent bone density loss?
Preventing bone density loss can be achieved through strategies such as regular weight-bearing exercises, consuming a calcium-rich diet, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy body weight.
Is it important to monitor bone density progress?
Yes, it is crucial to monitor bone density progress through regular bone density scans, especially for individuals at risk of osteoporosis or other bone-related conditions. This helps in assessing the effectiveness of treatments and making necessary adjustments to prevent further bone density loss.
Are there any specific strategies for maintaining bone health as you age?
Yes, there are several strategies for maintaining bone health as you age, including staying active, getting an adequate amount of vitamin D and calcium, avoiding falls, and consulting with healthcare providers for personalized recommendations based on individual health needs.
Related Links
What can I drink for good bones?What foods help bone repair?